Difference between revisions of "Guide to Atmospherics"
LordisMangis (talk | contribs) (→Where to Get Pipes: Added transit tubes as per PR #24739.) |
|||
| (54 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Rewrite|reason=This is due for a rewrite, it's rather short for explaining easily one of the most complex department/collection of mechanics we have available. Content is pretty much there but it could be laid out for new players a bit better and distinguish atmospherics between stations other than the NSS Cyberiad.}} | ||
|reason = | {{JobEngineering}}[[Atmospherics]]. To the ignorant, a mystical art indistinguishable from actual magic. To the (hopefully) educated [[Atmospheric Technician]]s of the station, a glorified network of conveyors for moving gases about. Either way, Atmospherics holds great and terrifying power in the hands of the initiated. | ||
==Pipes and Gases, the Basics of Atmos== | |||
If you aren't working with pipes and gases, you aren't doing atmospherics. | |||
===Where to Get Pipes=== | |||
Meet your two new friends. One never returns the money they borrow, you aren't really sure why you hang out with them. The other one is kind of awesome. | |||
[[File:rapid_pipe_dispenser.png|64px]] Rapid Pipe Dispenser - A handheld tool that can print, place and recycle pipes for you. Fits in your backpack and doesn't need ammo. | |||
Beneath are all the things your dispenser can make. Learn them well, for they are the fabric from which atmos is woven. | |||
<tabs> | |||
<tab name="Atmospheric Pipes"> | |||
= | {| class="wikitable mw-collapsible" style="width:80%" | ||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible | |||
|style="width:32px"|'''Items''' | |style="width:32px"|'''Items''' | ||
|style="width:15%"|'''Name''' | |style="width:15%"|'''Name''' | ||
|style="text-align:center;"|''' | |style="width:15%"|'''Description''' | ||
|style="text-align:center;"|'''Details''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Atmospheric_Pipe.png| | |[[File:Atmospheric_Pipe.png|64px]] | ||
| | |Normal Pipes | ||
|These are | |Generic pipes that can be used for most tasks. | ||
|These are airtight pipes that can carry any gas you pump into them. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:supply_pipe.png| | |[[File:supply_pipe.png|64px]] | ||
|Air Supply Pipe | |Air Supply Pipe | ||
|Used to distribute air all across the station. | |Used to distribute air all across the station. | ||
|Special pipes that are mostly used for the air distribution network. Can be laid in parallel to normal pipes and scrubber pipes. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:scrubber_pipe.png| | |[[File:scrubber_pipe.png|64px]] | ||
| | |Scrubbers Pipe | ||
| | |Used to move waste or harmful gases. | ||
|Special pipes that are mostly used for the waste network. Can be laid in parallel to normal pipes and air supply pipes. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:heat_exchanger_pipe.png| | |[[File:heat_exchanger_pipe.png|64px]] | ||
|Heat Exchange Pipe | |Heat Exchange Pipe | ||
| | |Shares heat between the pipe and the environment. | ||
|Exchanges heat between any gas in the pipe and any gas in the tile. Think space loop(for cooling) or the [[Toxins]] burn chamber(for heating). Connects to normal pipes via junctions. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:universal_pipe.png| | |[[File:universal_pipe.png|64px]] | ||
|Universal Pipe Adapter | |Universal Pipe Adapter | ||
|Used to | |Can be fitted to any pipe type. | ||
|Used to interface between normal, air supply, and scrubbers pipes. They cannot connect to each other without this. | |||
|} | |} | ||
</tab> | |||
= | <tab name="Atmospheric Devices"> | ||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible | {| class="wikitable mw-collapsible" style="width:80%" | ||
|style="width:32px"|'''Items''' | |style="width:32px"|'''Items''' | ||
|style="width:15%"|'''Name''' | |style="width:15%"|'''Name''' | ||
|style="text-align:center;"|''' | |style="width:15%"|'''Description''' | ||
|style="text-align:center;"|'''Details''' | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Vent_Port.png| | |[[File:Vent_Port.png|64px]] | ||
|Unary Vent | |Unary Vent | ||
| | |The standard vent used to distribute air. | ||
|Needs to be inside a blueprinted room with a functional air alarm to operate. Typically used to pump breathable air into a room. | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:Scrubber_Port.png|64px]] | |||
|Air Scrubber | |||
|Scrubs the air clean. | |||
|Needs to be inside a blueprinted room with a functional air alarm to operate. Can remove specific gases from the room it is in, or rapidly siphon out all gas. Typically used to remove harmful gases like CO2 from the station's air. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Vent_Port.png| | |[[File:Vent_Port.png|64px]] | ||
|Passive Vent | |Passive Vent | ||
|An | |An unpowered vent that relies on pipe pressure to operate. | ||
|Freely exchanges gas and heat between the tile and the connected pipe network, based on pressure and temperature gradients. Does not require power, or even a blueprinted room. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:dual_vent.png| | |[[File:dual_vent.png|64px]] | ||
|Dual-Port Air Vent | |Dual-Port Air Vent | ||
|Has a valve and pump attached to it. There are two ports | | | ||
|Has a valve and pump attached to it. There are two ports. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Connector_Port.png| | |[[File:Connector_Port.png|64px]] | ||
|Connector Port | |Connector Port | ||
| | |A connector port for canisters of gas. | ||
|Connects canisters to pipe networks. When used in conjunction with pumps, allows you to fill canisters or to empty them into a pipe network. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Pump.png| | |[[File:Pump.png|64px]] | ||
|Gas Pump | |Gas Pump | ||
| | |A generic pressure pump. | ||
|This pump is configured to measure how much gas it pumps by pressure. Can be set to only pump a certain amount of pressure through. The maximum pressure this pump can be set to move is 4500 kPa | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Volumetric_Pump.png| | |[[File:Volumetric_Pump.png|64px]] | ||
|Volume Pump | |Volume Pump | ||
| | |The gas pump's cool sibling. | ||
|This pump is configured to measure how much gas it pumps by volume instead of pressure. Can be set to pump only a specific volume of gas through. The maximum volume this pump can be set to move is 200L/s. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Passive_Gate.png| | |[[File:Passive_Gate.png|64px]] | ||
|Passive Gate | |Passive Gate | ||
| | |A passive one-way valve. | ||
|A valve that only lets gas pass through if the input pressure and the target setting are both higher than the output pressure and the input pressure is above the target setting. Can be set between 0 and 4500 kPa and does not require power. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Gas_Filter.png| | |[[File:Gas_Filter.png|64px]] | ||
|Gas Filter | |Gas Filter | ||
|Checks for whatever gas you set it to, then filters it out into another pipe | |Separates out gases. | ||
|A scrubber in pipe form. Checks for whatever gas you set it to, then filters it out into another pipe. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Gas_Mixer.png| | |[[File:Gas_Mixer.png|64px]] | ||
|Gas Mixer | |Gas Mixer | ||
| | |Mixes gases together. | ||
|The opposite of a filter. Takes the contents of its two inputs and combines them together at whatever ratio you tell it to, then pumps them through the output. Importantly, ratios are measured by pressure, not volume. Maximum output pressure is 4500 kPa | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:Heat_exchanger.png|64px]] | |||
|Heat Exchanger | |||
|Equalize heat between two pipe networks. | |||
|When two heat exchangers are placed next to each other, facing each other, they will try to equalize the heat between the two pipe networks they are connected to. They connect to normal pipes and thus are not part of the heat exchanger pipe system. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Air_Injector.png| | |[[File:Air_Injector.png|64px]] | ||
|Air Injector | |Air Injector | ||
|Used to | |Used to force gases into high pressure areas. | ||
|A gas injector that will continue to pump its contents out regardless of how high the pressure around it is. Measures how much it pumps by volume. Will not operate without being linked to a console. Will display a green light when on. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Manual_Valve.png| | |[[File:Manual_Valve.png|64px]] | ||
|Manual Valve | |Manual Valve | ||
|A manually-controlled valve, it requires no power and also no ID | |A simple hand-turned gas valve. | ||
|A manually-controlled valve, it requires no power and also no ID authorization to use. Doesn't require power(or a blueprinted room), doesn't require ID access, and cannot be operated by the AI, borgs, or drones. Displays a small green light when open. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Digital_Valve.png| | |[[File:Digital_Valve.png|64px]] | ||
|Digital Valve | |Digital Valve | ||
|An electronically-controlled gas valve. | |An electronic valve. | ||
|An electronically-controlled gas valve. Requires power, requires ID access, and can be operated by the AI, borgs, and drones. Displays a small green light when open. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:meter.gif| | |[[File:meter.gif|64px]] | ||
|Meter | |Meter | ||
| | |Measures temperature and pressure inside the pipe it's on. | ||
|Simply place over any flat stretch of pipe and wrench it on. Upon examination, it should now be yielding measurements on what is going on inside the pipe. Does not provide as much information as an analyser/gas scanner, but good for being able to tell what is going on at a glance. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Gas_Sensor.png| | |[[File:Gas_Sensor.png|64px]] | ||
|Gas Sensor | |Gas Sensor | ||
|Used to sense the pressure and temperature of the gas surrounding the sensor itself, rather than a pipe. | |Senses gas. No, really. | ||
|Used to sense the pressure and temperature of the gas surrounding the sensor itself, rather than a pipe. Must be connected to one of several kinds of computer to be used. | |||
|} | |} | ||
</tab> | |||
= | <tab name="Disposal Pipes"> | ||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible" style="width:80%" | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible | |||
|style="width:32px"|'''Items''' | |style="width:32px"|'''Items''' | ||
|style="width:15%"|'''Name''' | |style="width:15%"|'''Name''' | ||
|style="text-align:center;"|'''Description''' | |style="text-align:center;"|'''Description''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Disposal_pipe.png| | |[[File:Disposal_pipe.png|64px]] | ||
|Disposal Pipe | |Disposal Pipe | ||
| | |Large pneumatic pipes that are used to carry trash, mail, and occasionally people around the station. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Disposal_bin.png| | |[[File:Disposal_bin.png|64px]] | ||
|Disposal Bin | |Disposal Bin | ||
| | |The preferred method for delivering garbage into disposal pipes. Holds onto contents until they are flushed, whether manually or automatically. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Disposal_outlet.png| | |[[File:Disposal_outlet.png|64px]] | ||
|Disposal Outlet | |Disposal Outlet | ||
|Whenever someone | |Whenever something or someone has reached this from a disposal pipe, they are ejected after a buzzer sounds. | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Disposal_intake.png| | |[[File:Disposal_intake.png|64px]] | ||
|Disposal Intake | |Disposal Intake | ||
| | |An open chute into disposal pipes. Objects or people that enter will be sent into connected disposal pipes. Objects or people who reach one of these at the end of a disposal pipe are ejected at high speed in a random direction. | ||
|} | |} | ||
</tab> | |||
<tab name="Transit Tubes"> | |||
{| class="wikitable mw-collapsible" style="width:80%" | |||
|style="width:32px"|'''Items''' | |||
|style="width:15%"|'''Name''' | |||
|style="text-align:center;"|'''Description''' | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:Transit_Tube.png|64px]] | |||
|Transit Tube | |||
|A glass tube used for transportation with the use of transit pods. | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:Diagonal_Transit_Tube.png|64px]] | |||
|Diagonal Transit Tube | |||
|A glass tube used for transportation with the use of transit pods. This one is diagonal. | |||
|- | |||
||[[File:Curved_Transit_Tube.png|64px]] | |||
|Curved Transit Tube | |||
|A glass tube used for transportation with the use of transit pods. This one is curved | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:Junction_Transit_Tube.png|64px]] | |||
|Junction Transit Tube | |||
|A glass tube used for transportation with the use of transit pods. This one has three sides. You can hold down a directional key to choose which side to go to. | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:Transit_Tube_Station.png|64px]] | |||
|Transit Tube Station | |||
|A station for transit pods to park in midway through the ride, letting the person leave by pressing the directional key the exit is facing in or going through the station faster by pressing a directional key where the next transit tube is. You can board it by walking in through it's entrance. It's density prevents people or bullets from passing through it. | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:Terminus_Dispenser_Tube_Station.png|64px]] | |||
|Terminus Dispenser Tube Station | |||
|A terminus used to signify the end or beginning of a transit tube network. It can be boarded it by walking in through it's entrance. This one creates and recycles transit pods. | |||
|- | |||
|[[File:Dispenser_Tube_Station.png|64px]] | |||
|Dispenser Tube Station | |||
|A station for transit pods to park in midway through the ride, letting the person leave by pressing the directional key the exit is facing in or going through the station faster by pressing a directional key where the next transit tube is. It can be boarded it by walking in through it's entrance. This one creates and recycles transit pods. It's density prevents people or bullets from passing through it. | |||
|- | |||
</tab></tabs> | |||
===The Gases=== | |||
The main goal of atmospherics is to manipulate these in a way that benefits the station. Each type of gas has different properties that can help or hinder. Your skill in manipulating these will determine the success of your atmospheric machinations. | |||
{|class="wikitable" style="width:80%;" | |||
|'''Nitrogen (N2)''' | |||
|Nitrogen is an inert gas that makes up 80% of the air on the station. Vox breathe this, but in the station atmosphere, it mostly just takes up space. | |||
|- | |||
|'''Oxygen (O2)''' | |||
|The other 20% of the air. Most of the crew will be needing at least 16kPa of this stuff in the atmosphere in order to live. Poisonous to Vox and Plasmamen. Necessary for burning plasma. | |||
|- | |||
|'''Air''' | |||
|You know what this is. The gas mix that is distributed around the station. It is composed of 80% N2 and 20% O2. | |||
|- | |||
|'''CO2''' | |||
|An invisible gas that is slightly heavier than air. This is what crewmembers who breathe will be exhaling. Also produced by plasma fires. In high concentrations, will make you pass out, which can quickly lead to suffocation. | |||
|- | |||
|'''Nitrous Oxide (N2O)''' | |||
|A white-flecked gas that is slightly heavier than CO2. At low concentrations, will cause sporadic laughing. At high concentrations, will put you to sleep. | |||
|- | |||
|'''Plasma (Toxins)''' | |||
|The oil of the new world. Purple, highly flammable, and highly toxic(unless you are a Plasmaman). Burns with oxygen and will spontaneously ignite with it at a high enough temperature. Much heavier than all the previous gases. | |||
|- | |||
|'''???''' | |||
|Hmmmm... | |||
|} | |||
==Station Systems== | |||
While pipes themselves will always work if undamaged, atmospheric devices all have certain prerequisites that must be met for them to operate. | |||
Remember, almost all atmos devices require a powered APC to work. | |||
In addition, there are other pieces of infrastructure that can/must be used when working with specific atmospheric devices. | |||
===[[Air Alarm]]=== | |||
[[File:AirAlarm.png|64px]] | |||
Mandatory for the use of non-passive vents and scrubbers. Allows a wide range of control over a blueprinted rooms current gas contents. Where exactly the Air Alarm is in the room does not matter. As long as the room is blueprinted and powered it will function. Cannot be placed in areas that are not blueprinted. | |||
''' | '''To learn more about Air Alarms and how to use them, click here: [[Air Alarm]]''' | ||
''' | |||
===Computers Consoles=== | |||
* '''Atmospheric Alert Computer:''' This computer console will tell you where your attention is needed. Green means everything is alright, yellow signals something is wrong, and red means things have gone wrong enough for an alarm to be triggered (Usually caused when a room's air stops being breathable). | |||
* '''Central Atmospherics Computer:''' Allows remote control of any air alarm on the station that has remote access enabled. | |||
* '''The Distribution Computers:''' A console to monitor gas storage contents, control air injectors/extraction vents, etc. If you understand how to use these properly, you probably know what you are doing. Air Injectors REQUIRE these to work. | |||
===Thermomachine=== | |||
Used to change the temperature of gases in pipes, thermomachines are essential to any successful TEG. | |||
==Atmosia Proper - The Beating Heart of the Station== | |||
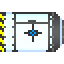
[[File:Atmosia_and_Air_Loop_Diagram.jpg|1300px|thumb|center|Left - Atmosia with non-air systems faded out; Right - Simplified diagram of the Air Processing System in Atmosia]] | |||
In Atmosia, you will see many different colored pipes. These colors are labels, marking out different systems within atmosia. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:80%;" | |||
!style="width:10%"|Name | |||
!style="text-align:center;"|Description | |||
|- | |||
!Air Supply <br> [[File:supply_pipe.png|32px]] | |||
|The dark blue pipe is the '''Main Air Supply'''. It sends breathable air (roughly 80% nitrogen and 20% oxygen) to all the vents on the station, and is fed by the cyan pipe in Atmospherics. | |||
|- | |||
!Scrubber <br> [[File:Scrubber_pipe.png|32px]] | |||
|The red pipe is the '''Scrubber Pipe'''. This is where all the toxic waste normally ends up by the scrubber system found all around the station. It may contain breathable air, however it is unfiltered and possibly contaminated. | |||
|- | |||
!Air Mix <br> [[File:cyan_pipe.png|32px]] | |||
|The cyan pipe is the breathable air or the '''Air Mix'''. This pipe feeds into the main air supply. | |||
|- | |||
!Waste <br> [[File:purple_pipe.png|32px]] | |||
|The purple pipe is the '''Waste Pipe''', which retrieves waste air from the scrubber pipe which then leads to the filter. | |||
|- | |||
!Filter <br> [[File:green_pipe.png|32px]] | |||
|The green pipe is the '''Filter Pipe''', which filters out the various gases in the waste air provided by the water at various filters placed along it. Each filter puts the respect gases back into the gas containers. | |||
|- | |||
!Pure <br> [[File:yellow_pipe.png|32px]] | |||
|The yellow pipe is the '''Mix Pipe''', which is internal to Atmospherics and is used for custom air mixes. | |||
|} | |||
==The Basic Mathematical Details== | |||
===Ideal Gas Law=== | ===Ideal Gas Law=== | ||
The magical formula for improving your burn mixes.... and explaining why your coolant pipes have such a low pressure. | |||
Formula: '''PV=nRT''' | Formula: '''PV=nRT''' | ||
| Line 227: | Line 295: | ||
'''T''' - Temperature in Kelvin<br> | '''T''' - Temperature in Kelvin<br> | ||
Cooling a gas will make it take up less space (volume) for each unit (mole) of said gas. | |||
This effect also results in a gas at a lower temperature having a lower pressure. | |||
Heating a gas will have the opposite effect, resulting in a larger volume and higher pressure per mole. | |||
===Conversion to and from Kelvin=== | |||
While most things will yield temperature in both Kelvin and Celsius, here is the conversion formula just in case. | |||
Formula: '''K = C + 273.15''' | |||
'''C''' - Celsius<br> | |||
'''K''' - Kelvin | |||
(Temperature in Kelvin minus 273.15 is that same temperature, but in Celsius) | |||
==Additional Guides== | ==Additional Guides== | ||
*[[File:Gasturbine.png|32px|link= | *[[File:Gasturbine.png|32px|link=Gas Turbine]] [[Gas Turbine|Guide to Gas Turbine]] | ||
*[[File:Supermatter.png | *[[File:Thermoelectric_Generator.gif|link=Thermoelectric Generator|32px]] [[Thermoelectric Generator|Guide to Thermoelectric Generator]] | ||
*[[File:Supermatter.png|link=Supermatter Engine|32px]] [[Supermatter Engine|Guide to Supermatter Engine]] | |||
*[[File:AirAlarm.png|link=Air Alarm|32px]] [[Air Alarm|Guide to Air Alarms]] | |||
==Related Links== | ==Related Links== | ||
*[[ | *[[Atmospheric Technician]] | ||
[[Category:Guides]] | [[Category:Guides]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:45, 27 March 2024
REASON: This is due for a rewrite, it's rather short for explaining easily one of the most complex department/collection of mechanics we have available. Content is pretty much there but it could be laid out for new players a bit better and distinguish atmospherics between stations other than the NSS Cyberiad.
Departmental Head
Chief Engineer
Atmospherics. To the ignorant, a mystical art indistinguishable from actual magic. To the (hopefully) educated Atmospheric Technicians of the station, a glorified network of conveyors for moving gases about. Either way, Atmospherics holds great and terrifying power in the hands of the initiated.
Pipes and Gases, the Basics of Atmos
If you aren't working with pipes and gases, you aren't doing atmospherics.
Where to Get Pipes
Meet your two new friends. One never returns the money they borrow, you aren't really sure why you hang out with them. The other one is kind of awesome.
 Rapid Pipe Dispenser - A handheld tool that can print, place and recycle pipes for you. Fits in your backpack and doesn't need ammo.
Rapid Pipe Dispenser - A handheld tool that can print, place and recycle pipes for you. Fits in your backpack and doesn't need ammo.
Beneath are all the things your dispenser can make. Learn them well, for they are the fabric from which atmos is woven.
| Items | Name | Description | Details |
|
Normal Pipes | Generic pipes that can be used for most tasks. | These are airtight pipes that can carry any gas you pump into them. |

|
Air Supply Pipe | Used to distribute air all across the station. | Special pipes that are mostly used for the air distribution network. Can be laid in parallel to normal pipes and scrubber pipes. |

|
Scrubbers Pipe | Used to move waste or harmful gases. | Special pipes that are mostly used for the waste network. Can be laid in parallel to normal pipes and air supply pipes. |
|
Heat Exchange Pipe | Shares heat between the pipe and the environment. | Exchanges heat between any gas in the pipe and any gas in the tile. Think space loop(for cooling) or the Toxins burn chamber(for heating). Connects to normal pipes via junctions. |
|
Universal Pipe Adapter | Can be fitted to any pipe type. | Used to interface between normal, air supply, and scrubbers pipes. They cannot connect to each other without this. |
The Gases
The main goal of atmospherics is to manipulate these in a way that benefits the station. Each type of gas has different properties that can help or hinder. Your skill in manipulating these will determine the success of your atmospheric machinations.
| Nitrogen (N2) | Nitrogen is an inert gas that makes up 80% of the air on the station. Vox breathe this, but in the station atmosphere, it mostly just takes up space. |
| Oxygen (O2) | The other 20% of the air. Most of the crew will be needing at least 16kPa of this stuff in the atmosphere in order to live. Poisonous to Vox and Plasmamen. Necessary for burning plasma. |
| Air | You know what this is. The gas mix that is distributed around the station. It is composed of 80% N2 and 20% O2. |
| CO2 | An invisible gas that is slightly heavier than air. This is what crewmembers who breathe will be exhaling. Also produced by plasma fires. In high concentrations, will make you pass out, which can quickly lead to suffocation. |
| Nitrous Oxide (N2O) | A white-flecked gas that is slightly heavier than CO2. At low concentrations, will cause sporadic laughing. At high concentrations, will put you to sleep. |
| Plasma (Toxins) | The oil of the new world. Purple, highly flammable, and highly toxic(unless you are a Plasmaman). Burns with oxygen and will spontaneously ignite with it at a high enough temperature. Much heavier than all the previous gases. |
| ??? | Hmmmm... |
Station Systems
While pipes themselves will always work if undamaged, atmospheric devices all have certain prerequisites that must be met for them to operate.
Remember, almost all atmos devices require a powered APC to work.
In addition, there are other pieces of infrastructure that can/must be used when working with specific atmospheric devices.
Air Alarm
Mandatory for the use of non-passive vents and scrubbers. Allows a wide range of control over a blueprinted rooms current gas contents. Where exactly the Air Alarm is in the room does not matter. As long as the room is blueprinted and powered it will function. Cannot be placed in areas that are not blueprinted.
To learn more about Air Alarms and how to use them, click here: Air Alarm
Computers Consoles
- Atmospheric Alert Computer: This computer console will tell you where your attention is needed. Green means everything is alright, yellow signals something is wrong, and red means things have gone wrong enough for an alarm to be triggered (Usually caused when a room's air stops being breathable).
- Central Atmospherics Computer: Allows remote control of any air alarm on the station that has remote access enabled.
- The Distribution Computers: A console to monitor gas storage contents, control air injectors/extraction vents, etc. If you understand how to use these properly, you probably know what you are doing. Air Injectors REQUIRE these to work.
Thermomachine
Used to change the temperature of gases in pipes, thermomachines are essential to any successful TEG.
Atmosia Proper - The Beating Heart of the Station
In Atmosia, you will see many different colored pipes. These colors are labels, marking out different systems within atmosia.
The Basic Mathematical Details
Ideal Gas Law
The magical formula for improving your burn mixes.... and explaining why your coolant pipes have such a low pressure.
Formula: PV=nRT
P - Pressure in kilopascals or kPa
V - Volume in liters
n - is the amount of substance of gas (also known as number of moles)
R - is a constant or 8.31
T - Temperature in Kelvin
Cooling a gas will make it take up less space (volume) for each unit (mole) of said gas. This effect also results in a gas at a lower temperature having a lower pressure. Heating a gas will have the opposite effect, resulting in a larger volume and higher pressure per mole.
Conversion to and from Kelvin
While most things will yield temperature in both Kelvin and Celsius, here is the conversion formula just in case.
Formula: K = C + 273.15
C - Celsius
K - Kelvin
(Temperature in Kelvin minus 273.15 is that same temperature, but in Celsius)
Additional Guides
 Guide to Gas Turbine
Guide to Gas Turbine Guide to Thermoelectric Generator
Guide to Thermoelectric Generator Guide to Supermatter Engine
Guide to Supermatter Engine Guide to Air Alarms
Guide to Air Alarms