Difference between revisions of "User:Krossarn"
| Line 262: | Line 262: | ||
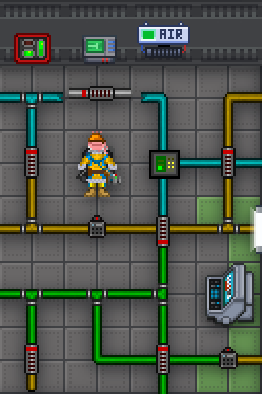
===Colour Coded Pipes=== | ===Colour Coded Pipes=== | ||
===Atmospherics Layout=== | ===Atmospherics Layout=== | ||
= | |||
<tabs> | |||
= | <tab name="NSS Cyberiad"> | ||
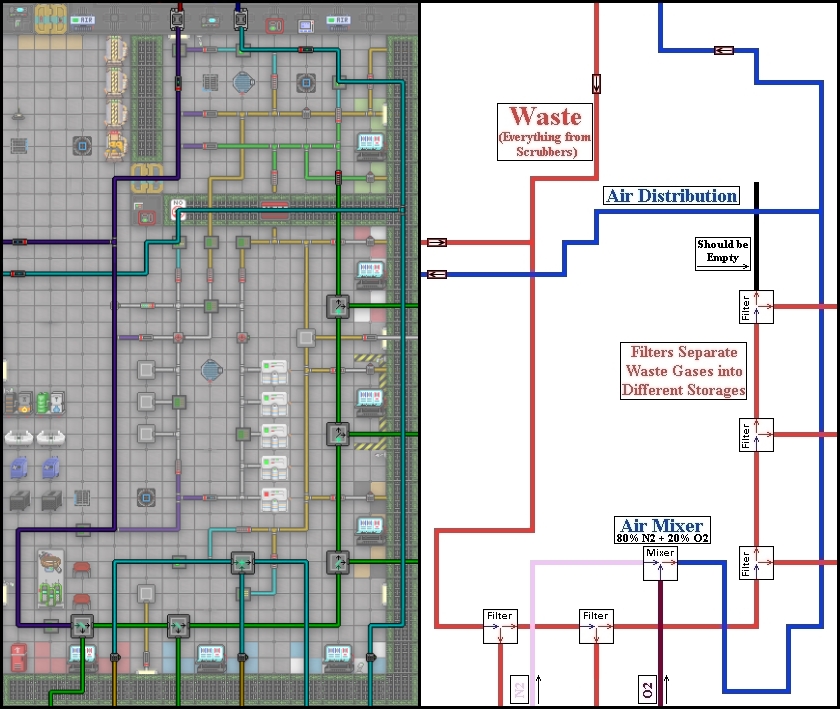
The layout of NSS Cyberiad, aka Boxstation. <br> | |||
[[File:Atmosia and Air Loop Diagram.jpg|Test]] | |||
</tab> | |||
<tab name="NSS Cyberiad Simplified"> | |||
A Simplified version of NSS Cyberiads Air distrobution system. <br> | |||
[[File:Atmosia and Air Loop Diagram.jpg|Test]] | |||
</tab> | |||
<tab name="NSS Kerberos"> | |||
The layout of NSS Kereberos, aka Deltastation. <br> | |||
[[File:Atmosia and Air Loop Diagram.jpg|Test]] | |||
</tab> | |||
<tab name="NSS Kerberos Simplified"> | |||
A Simplified version of NSS Kereberos Air distrobution system. <br> | |||
[[File:Atmosia and Air Loop Diagram.jpg|Test]] | |||
</tab> | |||
<tab name="NSS Cereberon"> | |||
The layout of NSS Cereberon, aka Metastation. <br> | |||
[[File:Atmosia and Air Loop Diagram.jpg|Test]] | |||
</tab> | |||
<tab name="NSS Cereberon Simplified"> | |||
A Simplified version of NSS Cereberon Air distrobution system. <br> | |||
[[File:Atmosia and Air Loop Diagram.jpg|Test]] | |||
</tab> | |||
</tabs> | |||
===Mixing Gases=== | ===Mixing Gases=== | ||
====Gas For Canisters==== | ====Gas For Canisters==== | ||
Revision as of 11:30, 2 January 2023
Departmental Head
Chief Engineer
Welcome to Atmospherics. Considered by many as one of the most diffcult profession to master on the station, while also being one of the most dangerous. The learning curve of Atmospherics is rather steep, its important to be patient and not losing focus. An Atmospheric Technician should be able to handle a few situations: Setting up Atmospherics properly, repressurise a room, remove dangerous gases in unwanted areas, mix and transport gases.
The jobs main focus is of course around the various gases found on the station. The Atmospheric Technician should know how the different gases works and how to manipulate them for the saftey of the station and for their own little projects. Having proper knowledge over the pipes and devices is key for managing the gases.
Working as an Atmospheric Technician can go from having a calm shift while working on a project or the station goal; into having to fix multiple breaches, repressurise several areas and fight fires all over the station, all at the same time. Knowledge over how to fix atmospheric issues is a must to ease the working condition for the rest of the crew.
The Basics Of Atmospherics
The first thing the technician need to understand is how to use the different available equipment to manipulate the atmospheric gases.
Tools and pipes are ever so important to even begin working with the basics of atmospherics.
Atmospherics Tools
| Item | Description |
Rapid Pipe Dispenser 
|
A handheld tool that can print, place and recycle pipes. Fits in a backpack or coat and doesn't need ammo. |
|---|---|
ATMOS Holofan 
|
Can project up to 3 holographic barriers which block gas movement. These holofans can be used to isolate breaches or prevent a spill from getting worse. Does not hold in high temperatures or in fires. |
Analyzer 
|
Mostly used for scanning the surrounding air and measuring the gas content and composition of pipes and canisters. A PDA with the breathe deep cartridge can also scan pipes and canisters. |
Multitool 
|
The multitool is used for many things. But for the atmospheric technician it's mostly used to link devices to monitors or an air alarm. |
Rapid Pipe Dispenser
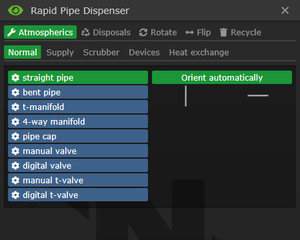
The Rapid Pipe Dispenser, aka RPD for short, will be one of the main tools for the technician to use. This device can rapidly dispense atmospherics and disposals piping, manipulate loose piping, and recycle any detached pipes it is applied to.
There are five main tabs and five subtabs in the RPDs menu where pipe types and pipe shapes can be selected as well as different pipe manipulations actions.
- Atmospherics
- Normal
- Supply
- Scrubber
- Devices
- Heat exchange
- Disposals
- Rotate
- Flip
- Recycle
It can also select which direction the pipe will be facing or have it orient automatically.
Alt + left clicking the RPD will bring up a small hud which can be used to switch rapidly between UI, rotate, flip and delete.
Atmospherics Pipes
There are a few different types of pipes on the station that the atmospheric technician will work with during their shift.
Standard Pipes
| Item | Description | Item | Description |
Normal Pipes 
|
Generic pipes that can be used for most tasks. These are airtight pipes that can carry any gas you pump into them. | Air Supply Pipe 
|
Special pipes that are mostly used for the air distribution network. Can be laid in parallel to normal pipes and scrubber pipes. Used to distribute air all across the station. |
|---|---|---|---|
Scrubber Pipes 
|
Special pipes that are mostly used for the waste network. Can be laid in parallel to normal pipes and air supply pipes. Used to move waste or harmful gases. | Heat Exchange Pipes 
|
Exchanges heat between any gas in the pipe and any gas in the tile. Think space loop(for cooling) or the Toxins burn chamber(for heating). Connects to normal pipes via junctions. |
Universal Pipes 
|
Used to interface between normal, air supply, and scrubbers pipes. They cannot connect to each other without this. | ||
Devices
Disposal Pipes
Gases
The main goal of atmospherics is to manipulate these in a way that benefits the station. Each type of gas has different properties that can help or hinder. Your skill in manipulating these will determine the success of your atmospheric machinations.
Station Systems
There are some systems on the station that the atmospheric technician will be working with during their shift.
Air Alarms
Mandatory for the use of non-passive vents and scrubbers. Allows a wide range of control over a blueprinted rooms current gas contents. Where exactly the Air Alarm is in the room does not matter. As long as the room is blueprinted and powered it will function. Cannot be placed in areas that are not blueprinted.
To learn more about Air Alarms and how to use them, click here: Air Alarm
Fire Alarms
Most areas have firelock doors which close if a fire is detected. It can be tempting to force them open (by resetting the fire alarm for the area) but bear in mind that doing so provides the fire with oxygen, which will keep it burning longer.
Computer Consoles And Monitors
Central Atmospherics Computer: The most important computer for the Atmospherics department to have. It can remotley access all air alarms on the station. Can also show a map with locations of all the air alarms.
Atmospheric Alert Computer: This computer will tell you where your attention is needed. Green means everything is alright, yellow signals something is wrong, and red means things have gone wrong enough for an alarm to be triggered (Usually caused when a room's air stops being breathable).
Large Tank Control: Can be used to monitor the pressure and control the inlet and outlet of larger tanks in Atmospherics. This computer is needed to be able to use the Injector.
Tank Monitor: Just like the Large Tank Control but will only connect to sensors, making it rather obsolete.
Link Devices To Monitors
To link different atmospheric devices, such as the air injector, a multitool is required. By using the multitool on the device a window will appear that will show what Frequency it's using, what it's named with an ID tag and the Multitool Buffer that links the device to the multitool. Not every device will have the option to add it to a multitool and some don't need to be added to a multitool at all.
The gas sensor have a few option on what information to show by enabling the different internal sensors with the multitool.
With the device added to the multitool it is now possible to link it to preferably a Large Tank Control. Use the multitool on the computer and a new window will appear.
Frequency needs to be the same as the device for it to be able to link at all.
Input is where an air injector or unary vent can be linked with.
Output is for the unary vent with the siphon mode enabled.
Sensors only require to be on the same frequency to be linked to the gas sensor.
Atmospherics Machinery
Thermomachines
Atmospheric Portable Equipment
| Item | Description |
Space Heater 
|
Heating up a cold area. Find a nearby breach and turn it on once it's been repaired. Made by the Space Amish, it can reliably heat up a room to a habitable temperature. Can be adjusted. |
|---|---|
Portable Pump 
|
Filling a room with air or sucking the air out of a room. Set the pump direction to out, set the release pressure to maximum. Be sure to connect it to the blue-designated ports outside Engineering to fill it up with some delicious air-mix beforehand. Turn it on, and use it to carve the room's atmosphere to your desire. |
Portable Scrubber 
|
Cleaning the air from Plasma and other unwanted gasses. Can also used for emptying Plasma Tanks and Oxygen tanks. |